Breakfast White Cheese – 300gr
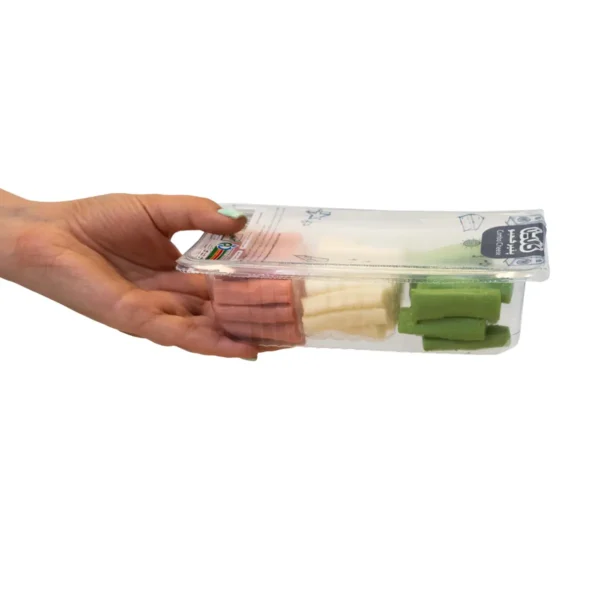
Combo Cheese Sticks – 180gr
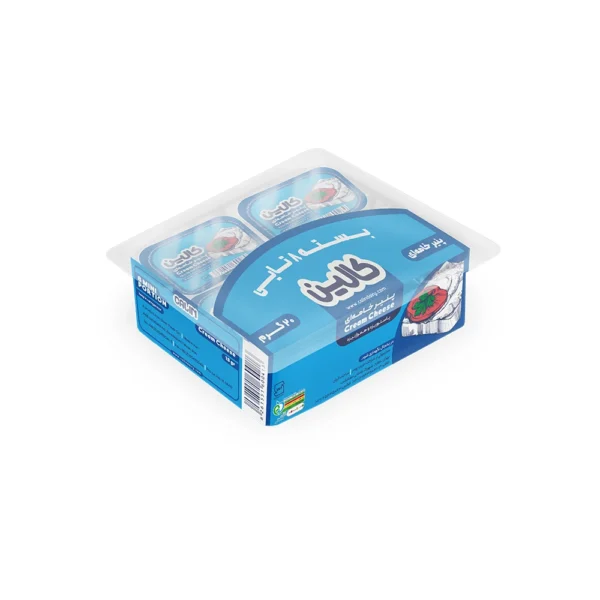
Combo Pack Cheese – 200gr
Combo Pack Cheese – 400gr
Process Cheese| Best Process Cheese Price
Processed cheese, also known as processed cheese product or processed cheese food, is a type of cheese made by blending natural cheeses with emulsifying salts. Unlike traditional cheese, processed cheese does not require aging and is immediately available for consumption after production. It has a smooth, uniform texture and melts easily, making it a popular choice for various culinary applications. Additionally, processed cheese has a longer shelf life than natural cheese and a distinct taste that differs from traditional aged cheeses.
Types of processed cheese
Calin offers a variety of processed cheeses to suit different tastes and culinary needs. These include our delicious stick cheese, perfect for slicing and serving with crackers or in sandwiches, breakfast cheese, ideal for spreading on toast or pairing with eggs, smoked cheese, which adds a rich, smoky flavor to any dish, and pizza cheese, designed to melt perfectly for a cheesy, gooey topping on your favorite pizzas. Each variety is crafted with the same high-quality ingredients, ensuring a smooth texture, rich flavor, and versatile use in various recipes.
Why Choose Processed Cheese
Processed cheese is widely consumed worldwide and is commonly known as American cheese in the United States. It is made by melting and blending natural cheese varieties such as cheddar or gouda with other ingredients, including emulsifiers, food coloring, and salt, to enhance its properties.
The origins of processed cheese date back to 1911 when Swiss inventor Walter Gerber first introduced it. However, in 1916, American entrepreneur James L. Kraft patented a version of processed cheese, leading to its mass production. By 1950, Kraft Foods had started selling individually wrapped cheese slices, which remain a staple in many households and fast-food chains today, particularly in cheeseburgers and sandwiches.
Advantages of Processed Cheese
Compared to natural cheese, processed cheese offers several benefits, including:
- Longer shelf life: Due to its stabilized composition, processed cheese lasts longer than natural cheese.
- Better melting properties: It melts evenly without separating or becoming oily.
- Consistent texture: The use of emulsifiers ensures a smooth and homogeneous texture.
- Easy to spread: Some varieties are designed for easy spreading on bread and crackers.
- Affordable price: Processed cheese is generally more cost-effective than many aged cheeses.
Ingredients Used in Processed Cheese
To achieve its distinct taste and texture, processed cheese contains a combination of the following ingredients:
- Fat sources: Cream, butter, vegetable oils, and other fats are added to enrich the cheese’s flavor and texture.
- Dairy components: Whey protein or curd may be included to enhance the nutritional value and consistency of the cheese.
- Emulsifying salts: These ingredients help bind the cheese proteins and prevent separation when melted.
- Flavoring agents and color additives: To improve the taste and visual appeal, food-grade flavorings and colorants are sometimes added.
The precise combination of these ingredients varies depending on the manufacturer and the intended use of the cheese. Calin process cheeses are of the best quality, made with carefully selected ingredients that ensure a smooth texture, rich flavor, and long shelf life. The balanced blend of fats, proteins, and emulsifiers used in Calin process cheeses guarantees that they melt evenly, making them ideal for a wide range of culinary applications, from sandwiches to sauces and beyond.
How to Use Processed Cheese
Due to its mild flavor, soft texture, and easy melting characteristics, processed cheese is used in various dishes, including:
Hot Dishes
- Pizza: Processed cheese is commonly used in commercial pizza production due to its ability to melt evenly.
- Lasagna: It enhances the structure and taste of lasagna by providing a creamy texture.
- Macaroni and Cheese: Processed cheese is often included in cheese sauces to create a smooth and rich consistency.
- Omelets: Shredded or sliced processed cheese can be added to omelets for extra flavor.
- Grilled Meats: Processed cheese slices are a popular addition to grilled sandwiches, burgers, and paninis.
Cold Dishes
- Sandwiches: Sliced processed cheese is a convenient and tasty option for making sandwiches.
- Salads: Shredded processed cheese can be sprinkled on salads for added flavor.
- Dips: Blended processed cheese can serve as a dip for vegetables, chips, or breadsticks.
- Appetizers: Soft processed cheese can be paired with cold cuts, fruits, or crackers as part of a cheese platter.
Desserts and Pastries
- Cheesecakes: Some types of processed cheese, such as cream cheese varieties, are used in cheesecake recipes.
- Tarts: Processed cheese can be used as a filling in sweet and savory tarts.
- Baklava: Some versions of baklava use processed cheese as a filling for a unique flavor profile.
- Refrigerated Desserts: Processed cheese can be incorporated into chilled desserts such as layered biscuit puddings and fruit parfaits.
Other Uses of Processed Cheese
Processed cheese is also utilized in:
- Bread baking: Shredded processed cheese can be added to the dough to enhance the flavor and texture of bread.
- Sauce preparation: It is commonly blended into sauces to create creamy and flavorful toppings for various dishes.
- Food industry applications: Processed cheese is widely used in ready-made and convenience foods due to its stability and extended shelf life.
Frequently Asked Questions About Processed Cheese
1. Does processed cheese melt easily?
Yes, processed cheese melts more smoothly than natural cheese, making it ideal for cooking and baking.
2. Is processed cheese healthier than natural cheese?
While processed cheese offers convenience and affordability, it often contains additives and emulsifiers that natural cheese does not. It is best consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
3. Can processed cheese be used as a substitute for natural cheese?
Yes, processed cheese can be used as a substitute in many recipes, though it may alter the final taste and texture of the dish.
Processed cheese remains a popular choice for a variety of meals due to its affordability, long shelf life, and excellent melting properties. Whether in a cheeseburger, pizza, or creamy dip, it continues to be a versatile ingredient in modern kitchens.